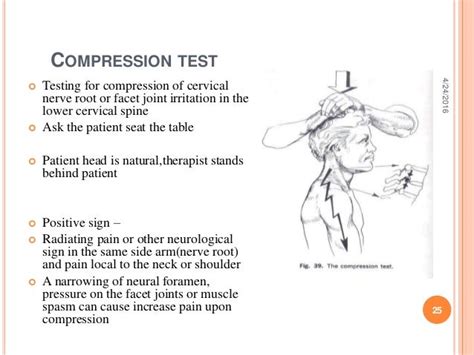
axial compression test cervical|foraminal compression special test : Big box store Although this test is commonly used for assessing cervical radiculopathy it is important due to its lower sensitivity that other tests are used in conjunction. In 2003, Dr. Robert . See more WEBMais Acompanhantes naregião deAltônia - PR. R$ 150/h. 23 anos. Com local. 2 reviews. Centro, Marechal Cândido Rondon - PR. -valor referente a uma finalização até meia hora completo. Oi sou Karine novinha, gatinha, buceta rosinha, apertada,dona de uns peitinhos lindos, sou baixinha branquinha pernas grossas, bem cavala um mulherão,faço .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Tipster page for Robin Goodfellow (Daily Mail) with informatio.
The Spurling's test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and Foraminal Compression Test) is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when looking for cervical nerve root compression causing Cervical Radiculopathy. See moreThere are different ways described in the literature to perform the Spurling's test. The version that provoked arm symptoms the best was with the . See more
Although this test is commonly used for assessing cervical radiculopathy it is important due to its lower sensitivity that other tests are used in conjunction. In 2003, Dr. Robert . See moreWhen performing an assessment it is important to know if the tool you are using is measuring what you want to measure that is Specificity and how good it is correctly identifying a pattern that is Sensitivityas both contribute to the diagnostic accuracy . See moreDe Hertogh WJ, Vaes PH, Vijverman V, De Cordt A, Duquet W. The clinical examination of neck pain patients: The validity of a group of tests.Manual Therapy. 2007; 12 (1): 50-5. Tong HC, Haig AJ, Yamakawa K. The Spurling test and cervical . See more The Spurling test helps a healthcare provider diagnose cervical radiculopathy (a pinched nerve in your neck). You might need this test if you have pain, numbness or muscle .
(2,3) The test is most commonly defined in current literature as passive cervical extension, ipsilateral rotation, and axial compression. (4) This summary contains information on use of the Spurling test in patients or clients .
The Spurling test helps to diagnose cervical radiculopathy. It’s also called the Spurling compression test or Spurling maneuver. Cervical radiculopathy occurs when a nerve .
The Spurling Test is designed to reproduce symptoms by compression of the affected nerve root. The cervical extension is used to induce/reproduce posterior bulging of the . The Spurling test is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess cervical nerve compression and radiculopathy. By reproducing or worsening symptoms through specific .After the initial examination, each subject, while seated, underwent six distinct provocative maneuvers of the cervical spine in the following order: lateral bending and axial compression, the original test described by Spurling and .
Doctors routinely use the Spurling test to check for cervical radiculopathy, which is the medical term for a compressed or pinched nerve in the neck. Cervical radiculopathy is common. Whenever cervical radiculopathy is suspected our observations suggest the staged provocative maneuvers that should be included in the physical evaluation are extension and .
The foraminal compression test or Spurling's test is statistically the best provocative test for confirming the diagnosis of cervical radiculopathy, when performed properly. It is performed by .
Other names: foraminal compression test, axial cervical compression test, quadrant test. How is the test performed? A doctor applies a downward pressure on the head of a patient who is seated with his/her neck .• Cervical Flexion Rotation Test • Cervical Compression, Jackson’s Compression, Maximum Foraminal . axial traction (cervical distraction) test, and Arm Squeeze test may be used to increase the likelihood . Cervical Orthopedic Tests Page 6 of 30 of a cervical radiculopathy, whereas a negative outcome of combined Upper Limb Neural .
After the initial examination, each subject, while seated, underwent six distinct provocative maneuvers of the cervical spine in the following order: lateral bending and axial compression, the original test described by Spurling and Scoville (Fig. 1 A); lateral bending, ipsilateral rotation and axial compression, also called the maximum . Introduction. The bilateral facet joints of the subaxial cervical spine play an important role in load-bearing and kinematics of the neck. They bear over 64% of axial load in the cervical spine 20,22 and are responsible for coupled intervertebral motions in axial rotation and lateral bending. 4,19 The facets also protect the spinal cord by preventing excessive .
*Empower your practice with our cutting-edge CE and CPD courses. Visit: https://www.educomcontinuingeducation.com• United States and Canada: https://www.chir.Whenever cervical radiculopathy is suspected our observations suggest the staged provocative maneuvers that should be included in the physical evaluation are extension and lateral bending first, followed by the addition of axial compression in cases with an inconclusive effect.
spurling test for cervical radiculopathy
Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.For the axial compression tests of the concrete blocks, a thin layer of cement plaster to correct the imperfections of settlement and of the materials was used. This procedure reduces defects that can generate stress concentrations. Reaction walls were used to test the structural masonry, according to the Brazilian Standard NBR 16522 [23].For the measurements of the strain, two .Spurling’s Test for Cervical Radicular Syndrome / Cervical Radiculopathy. Spurling’s test is a test with a low sensitivity of 50% and a good specificity of 83% to diagnose cervical radicular syndrome according to Wainner et al. (2003).Several authors have shown that this test has a rather low sensitivity and a high specificity. This test is also known by other names, including the Foraminal Compression test and Spurling’s test. This test should not be used if a significant cervical injury is suspected. With the patient in the seated position, tilt and rotate the patient’s neck to the side of involvement.
Flexion compression test. Procedure: The patient is seated. The examiner stands behind the patient and passively moves the cervical spine into flexion (tilts the patient’s head forward). Then axial compression is applied to the top of the head. Assessment: This is a good test of the integrity of the intervertebral disk. This is a corrected version of the article that appeared in print. Am Fam Physician. 2016;93(9):746-754 Patient information: See related handout on cervical radiculopathy, written by the authors .*Empower your practice with our cutting-edge CE and CPD courses. Visit: https://www.educomcontinuingeducation.com• United States and Canada: https://www.chir.Spurling's test involves compression of the cervical spine while it is slightly extended, rotated, and tilted toward one side. In a positive test, pain radiates distally, usually in a radicular distribution, indicating nerve root compression in the mid to lower cervical region. . Spurling (lateral flexion+rotation+axial compression); cervical .
The Kemp test (also known as the quadrant test and extension-rotation test) is a provocative test useful for diagnosing pain related to facet joint pathology, e.g. osteoarthritis.. The client performs combined extension and rotation of the . Cervical radiculopathy is a clinical condition characterized by unilateral arm pain, numbness and tingling in a dermatomal distribution in the hand, and weakness in specific muscle groups associated with a single . performed by rotating head toward the affected side, extending the neck, and then applying and axial load (downward pressure on the head) . for cervical spinal cord compression and myelopathy. test is positive when .

test standard for impact strength
Learn about the Spurling test, a diagnostic maneuver used to assess cervical nerve compression and radiculopathy. Understand the procedure, interpretation, and significance of this test in diagnosing cervical spine conditions and guiding appropriate treatment decisions. Study design: A comparative measurement design investigating the C4-Th1 intervertebral foramen under simulated clinical tests for cervical radiculopathy using magnetic resonance imaging. Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate functional changes in the cervical intervertebral foramen during the axial compression test (ACT), axial distraction . Axial neck pain is different from cervical radiculopathy and myelopathy. Axial cervical pain is also called uncomplicated neck pain, whiplash, neck strain, or cervical strain, and refers to pain .
"Cervical radiculopathy is a disease process marked by nerve compression from herniated disk material or arthritic bone spurs. This impingement typically produces neck and radiating arm pain or numbness, sensory deficits, or motor dysfunction in the neck and upper extremities.". Cervical radiculopathy occurs with pathologies that cause symptoms on the nerve roots. Our current understanding of cervical spine biomechanics in axial compression has been informed by impact tests using human cadaver spines or spine segments under various boundary conditions 7,8,9 .The Spurling test, also known as the Spurling maneuver, is a physical examination technique used to help diagnose cervical radiculopathy, which is a condition in which a nerve in the neck is compressed or irritated, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness in the arm or hand.. To perform the Spurling test, the examiner stands behind the seated patient and then extends . Spurling test, maximal cervical compression test, foraminal compression test, neck compression test, quadrant test [Abstract]. (2020).
After the initial examination, each subject, while seated, underwent six distinct provocative maneuvers of the cervical spine in the following order: lateral bending and axial compression, the original test described by Spurling and Scoville (Fig. 1A); lateral bending, ipsilateral rotation and axial compression, also called the maximum cervical .The cervical spine has sacrificed stability for mobility and is therefore vulnerable to injury. The craniocervical junction (atlanto-occipital joint), the lower atlanto-axial joint and other cervical segments are reinforced by internal as well as external ligaments.They secure the spinal stability of the cervical spine as a whole, together with surrounding postural muscles and allow .validity of Spurling’s Neck Compression Test in diagnosing cervical radiculopathy, along with the Axial Manual Traction and Shoulder Abduction tests. Forty-three . occiput and chin and applies axial traction force. Positive test is relief or reduction of cervical radicular symptoms. Viikari-Juntura (6) 1987 Supine position. 10-15 Kg traction
test that happened in thomas jeffersons family that impacted him
OFICIAL DROID. INOVE SEU CONHECIMENTO. INÍCIO. A.
axial compression test cervical|foraminal compression special test